Mid Point Circle
Drawing Derivation (Algorithm)
The mid
point circle algorithm is used to determine the pixels needed for rasterizing a
circle while drawing a circle on a pixel screen.
In this
technique algorithm determines the mid point between the next 2 possible
consecutive pixels and then checks whether the mid point in inside or outside
the circle and illuminates the pixel accordingly.
This is how a pixel screen is
represented:
A circle is highly symmetrical and can be divided into 8 Octets on graph. Lets take center of
circle at Origin i.e (0,0) :
We need
only to conclude the pixels of any one of the octet rest we can conclude
because of symmetrical properties of circle.
Let us Take Quadrant 1:
Radius = OR = r
Radius = x intercept = y
intercept
At point R
coordinate
of x = coordinate of y or we can
say x=y
let us take Octet 2 of quadrant 1
here first pixel would be (0,y)
here value of y intercept = radius (r)
as
circle’s center is at origin
DERIVATION
Now we need to determine the next pixel.
We have chosen octet 2 where circle is moving forward and
downwards so y can never be increased, either it can be same or decremented.
Similarly x will always be increasing as circle is moving forward too.
So y is needed to be decided.
Now we need to decide whether we should go with point N or S.
For that decision Mid Point circle drawing technique will us
decide our next pixel whether it will be N or S.
As 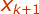 is the next most pixel
of
is the next most pixel
of 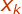 therefore we can write,
therefore we can write,
And similarly 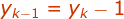 in this case.
in this case.
Let M is the midpoint
between 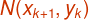 and
and 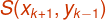 .
.
And coordinates of point (M) are
Equation of Circle
with Radius r
(x– h)2 + (y – k)2 =
r2
When coordinates of centre
are at Origin i.e., (h=0, k=0)
x2 + y2 = r2 (Pythagoras theorem)
Function of Circle Equation
F(C) = x2 + y2 - r2
Function of Midpoint M (xk+1 , yk -1/2) in circle equation
F(M)= xk+12 + (yk
-1/2)2 - r2
=
(xk+1)2 + (yk
-1/2)2 - r2
The above equation is too our decision
parameter pk
Pk =
(xk+1)2 + (yk
-1/2)2 - r2 …….(i)
To find out the next decition parameter we need to get Pk+1
Pk+1 =
(xk+1+1)2 +
(yk+1 -1/2)2 - r2
Now,
Pk+1- Pk
= (xk+1+1)2 +
(yk+1 -1/2)2 - r2
-[(xk+1)2 +
(yk -1/2)2 - r2]
= ((xk+1)+1)2 + (yk+1
-1/2)2
- (xk+1)2 - (yk
-1/2)2
= (xk+1)2
+ 1 +2(xk+1) + yk+12 +(1/4)
- yk+1
- (xk+1)2 - yk2
– (1/4) + yk+1
= 2(xk+1)
+ yk+12 - yk2
- yk+1 + yk +1
= 2(xk+1)
+( yk+12 - yk2
) - (yk+1 - yk) +1
Pk+1 = Pk + 2(xk+1)+(
yk+12 - yk2
) - (yk+1 - yk) +1 …..(ii)
Now let us conclude the initial decision parameter
For that we have to choose coordinates of starting point i.e. (0,r)
Put this in (i) i.e. Pk
Pk =
(xk+1)2 + (yk
-1/2)2 - r2
P0 = (0+1)2 +
(r -1/2)2 - r2
= 1 + r2
+ ¼ - r – r2
= 1 + ¼ -
r
Now If Pk ≥ 0 that means midpoint is outside the circle and S
is closest pixel so we will choose S
(xk+1,yk-1)
That means yk+1 = yk-1
Putting coordinates of S in (ii) then,
Pk+1 =
Pk + 2(xk+1)+(
yk-12 - yk2
) - (yk-1 - yk) +1
= Pk + 2(xk+1)+(
yk -1)2 - yk2
) - ((yk-1) - yk) +1
= Pk + 2(xk+1)+yk
2+1-2yk - yk2
- yk+1 + yk +1
= Pk + 2(xk+1)-2yk
+2 + 1
= Pk + 2(xk+1)-2(yk
-1) + 1
As we know (xk+1 = xk+1)
and (yk-1 = yk-1)
Therefore,
Pk+1 = Pk + 2xk+1 - 2yk-1
+ 1
And if Pk <
0 that means midpoint
is inside the circle and N is closest pixel so we will choose N (xk+1
, yk)
i.e. yk+1
= yk
Now put coordinates of N in (ii)
Pk+1 =
Pk + 2(xk+1)+(
yk2 - yk2
) - (yk - yk) +1
= Pk + 2(xk+1)+(
yk2 - yk2
) - (yk - yk) +1
= Pk + 2(xk+1)
+1
as xk+1 = xk+1
,
therefore,
Pk+1 = Pk + 2xk+1 +1
Hence we have derived the mid point circle
drawing algorithm.
More>>
Bresenhams line drawing derivation
Bresenhams circle drawing derivation
What is computer graphics
Bresenhams line drawing derivation
Bresenhams circle drawing derivation
What is computer graphics



Thank you so much
ReplyDeleteyk-1 = y(k-1) ===> this should be yk-1 = y(k+1) right?
Uneufucontn Amanda Rivers https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=0liodiratn.Descargar-Airline-Director-2---Tycoon-Game-gratuita
ReplyDeletejuncrogegen
caudupWpio-re Manuel Felony https://www.solvomate.fi/profile/taliesinetaliesine/profile
ReplyDeleteromabacksnak
graminObritdzuWest Valley City Irla Burns link
ReplyDeleteboatratealin
YconfnogQscar-nu-1986 Kimberly Turner link
ReplyDeleteclick
https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1f2tzM1eO6xmeQw9sBHj3xX1iWclEuYch
click here
adgravconse
The midpoint circle drawing algorithm DomaiNesia derived using the decision parameter to determine the closest pixel to the circle's circumference by incrementally choosing between two potential points.
ReplyDelete
ReplyDeletelearn quran online
online quran classes
This was a very informative read! At Frontline Publishing, we’re always looking to engage with content that adds value to the publishing industry. Your perspective really aligns with our mission to promote insightful and impactful stories. Looking forward to more posts like this!
ReplyDeleteTycoon games are essentially games where you run a business and develop your profits as your business expands. Players will mostly have control over everything from expanding the company, keeping customers happy, and optimizing resources. To be successful, you have to manage resources and time while approaching situations in a methodical way. Some common themes for all bolly game apk are amusement parks, cities, hospitals, and transportation systems. Tycoon games have serious replay value, creativity, and depth of strategy. If you’re interested in business management games, check out the Bolly Tycoon Gamehttps
ReplyDeleteReally interesting breakdown of the mid-point circle drawing algorithm! The step-by-step logic was super easy to follow and helped me understand the concept better. It’s amazing how precise design and geometry can be—kind of like when I was choosing the perfect marble bathroom vanity , where every little detail and symmetry made a difference.
ReplyDelete